Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Imai, Yasutomo*; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nuclear Technology, 210(5), p.814 - 835, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the study of safety enhancement on advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is essential to clarify the thermal-hydraulics under various operation conditions in a fuel assembly (FA) with the wire-wrapped fuel pins to assess the structural integrity of the fuel pin. A finite element thermal-hydraulics analysis code named SPIRAL has been developed to analyze the detailed thermal-hydraulics phenomena in a FA. In this study, the numerical simulations of the 37-pin bundle sodium experiments at different Re number conditions, including a transitional condition between laminar and turbulent flows and turbulent flow conditions, were performed to validate the hybrid turbulence model equipped in SPIRAL. The temperature distributions predicted by SPIRAL was consistent with those measured in the experiments. Through the validation study, the applicability of the hybrid turbulence model in SPIRAL to thermal-hydraulic evaluation of sodium-cooled FA in the wide range of Re number was confirmed.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Sugita, Yusuke; Yamaguchi, Yutaka
Nuclear Technology, 210(1), p.55 - 71, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study has developed an estimation method for residual sodium film and sodium lumps on dummy fuel pins in Monju and demonstrated sodium draining behavior through gaps among the pins, experimentally. The amounts of the residual sodium on the surface of the pins were measured using the three-type test specimens: (a) single pin, (b) 7-pin assembly, and (c) 169-pin assembly. The experiments revealed that the withdrawal speed of the pins and improvement of the sodium wetting increased drastically the amounts of the residual sodium. Furthermore, the experiments using the 169-pin assembly measured the practical amounts of the residual sodium in the dummy fuel assembly of short length and demonstrated sodium draining behavior through the dummy fuel assembly. The estimation method includes four models: a viscosity flow model, Landau-Levich-Derjaguin (LLD) model, an empirical equation related to the Bretherton model, and a capillary force model in a tube. The calculation predicted comparable amounts of the residual sodium with the experiments. An uncertain of the sodium wetting effects were close to 1.8 times the estimation values of the LLD model. With this estimation method, the amounts of the residual sodium on the unloaded Monju dummy fuel assembly can be evaluated.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-009, 165 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2020 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ito, Masahiro*; Ishitani, Ikuo*
JAEA-Technology 2023-006, 36 Pages, 2023/05
The BAMBOO code developed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is a computer code to analyze fuel pin bundle deformation in a fast reactor wire-spaced type fuel pin bundle subassembly. In this study we developed an analysis model to consider friction at the contact points between adjacent fuel pins, and at these between outermost fuel pins and a duct that are due to bundle-duct interaction. This model deals with friction forces at contact points in the contact and separation analysis of the code, and employs a convergent calculation where contact forces are gradually determined to avoid numerical instability when the friction occurs. Analyses of BAMBOO with the model showed very slight effects on the onset of contact between outer most pins and a duct, and on directions of pin displacements, within the range of practical friction coefficients.
Ono, Ayako; Yamashita, Susumu; Sakashita, Hiroto*; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing the computational fluid dynamics code, JUPITER, based on the volume of fluid (VOF) method to analyze detailed thermal-hydraulics in a reactor. The detailed numerical simulation of boiling from a heating surface needs a substantial computational cost to resolve the microscale thermal-hydraulic phenomena such as the bubble generation from a cavity and evaporation of a micro-layer. This study developed the simplified boiling model from the heating surface to reduce the computational cost, which will apply to the detailed simulation code based on the surface tracking method such as JUPITER. We applied the simplified boiling model to JUPITER, and compared the simulation results with the experimental data of the vertical heating surface in the forced convection. We confirmed the degree of their reproducibility, and the issues to be modified were extracted.
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Horiguchi, Naoki; Ono, Ayako; Furuichi, Hajime*; Katono, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2022/08
Ono, Ayako; Yamashita, Susumu; Sakashita, Hiroto*; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Dai-26-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/07
JAEA is implementing a simulation of a two-phase flow in the reactor core by TPFIT and JUPITER which are developed by JAEA based on the surface tracking method. However, it is impossible to simulate a boiling on the heating surface in the large-scale domain by this type of simulation method since the simulation of boiling based on the surface tracking method needs the fine mesh which sufficiently resolves the initiation of boiling. Therefore, JAEA started to develop the simplified boiling model applied for the two-phase flow in the fuel assemblies. In this study, the simulation results of the convection boiling on a vertical heating surface and the comparison between the simulation results and experimental results are shown.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2021-067, 135 Pages, 2022/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Fukushima Technology Development and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each departments manage facilities and develop related technologies to achieve the "Middle-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2017 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by the Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Materials Sciences Research Center, and development activities of Nuclear Human Resources Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Ina, Takuya; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 13th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Heterogeneous Systems (ScalAH22) (Internet), p.10 - 17, 2022/00
The ensemble data assimilation of computational fluid dynamics simulations based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) is implemented and optimized on a GPU supercomputer based on NVIDIA A100 GPUs. To connect the LBM and LETKF parts, data transpose communication is optimized by overlapping computation, file I/O, and communication based on data dependency in each LETKF kernel. In two dimensional forced isotropic turbulence simulations with the ensemble size of 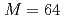 and the number of grid points of
and the number of grid points of 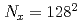 , the optimized implementation achieved
, the optimized implementation achieved 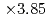 speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of
speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of 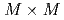 real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and
real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and 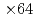 speedup was achieved.
speedup was achieved.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2021-006, 248 Pages, 2021/12
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Fukushima Technology Development and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Middle and long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2015 and 2016 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Material Science Research Center, and development activities of Nuclear Human Resources Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Junichi*; Ito, Masahiro*; Ishitani, Ikuo*; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Otsuka, Satoshi
Nuclear Technology, 207(8), p.1280 - 1289, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:34.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)Computer codes for irradiation behavior analysis of a fuel pin and a fuel pin bundle and for coolant thermal hydraulics analysis were coupled into an integrated code system. In the system, each code provides data required by other codes and the analyzed results are shared among them. The system allows for the synthesizing of analyses of thermal, chemical and mechanical behaviors in a fuel subassembly under irradiation. A test analysis was made for a fuel subassembly containing a mixed oxide fuel pin bundle irradiated in a fast reactor. The results of the analysis were presented with transverse cross-sectional images of the fuel subassembly and three-dimensional images of a fuel pin and fuel pin bundle models. For detailed evaluation, various irradiation behaviors of all fuel pins in the subassembly were analyzed and correlated with irradiation conditions.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Oizumi, Akito; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hayes, D.*; Hutchinson, J.*; McKenzie, G.*; McSpaden, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 194(2), p.138 - 153, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worth was conducted systematically in three fast spectra with different fuel compositions on the Comet critical assembly of the National Criticality Experiments Research Center. Previous experiments in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb and a low-enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb systems had been performed in 2016 and 2017, respectively. A follow-on experiment in a plutonium (Pu)/Pb system has been completed. The Pu/Pb system was constructed using lead plates and weapons grade plutonium plates that had been used in the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) of Argonne National Laboratory until the 1990s. Furthermore, the HEU/Pb system was re-examined on the Comet critical assembly installed newly with a device that can guarantee the gap reproducibility with a higher accuracy and precision, and then the experimental data was re evaluated. Using the lead void reactivity worth measured in these three cores with different fuel compositions, the latest nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VIII.0, were tested with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP version 6.1. As a result, the calculations by ENDF/B-VIII.0 were confirmed to agree with lead void reactivity worth measured in all the cores. It was furthermore found that the calculations by JENDL 4.0 overestimate by more than 20% for the Pu/Pb core while being in good agreements for the HEU/Pb and LEU/Pb cores.
Ono, Ayako; Yamashita, Susumu; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.666 - 677, 2019/08
An evaluation methodology of critical heat fluxes (CHFs) based on a mechanism for fuel assemblies in light water reactors (LWRs) is needed in order to design and evaluate the safety for the fuel assemblies in LWRs. In our study, the numerical simulation with surface-tracking will be applied for the two-phase flow in fuel assemblies in order to obtain the detail data relating to the size and velocity of bubbles in the subchannel, which is needed to predict the CHF based on the mechanism. In this study, the numerical simulation of two-phase flow in 4 4 bundle was implemented by using JUPITER in order to establish the evaluation method of the size and velocity of bubbles by the numerical simulation, which is the multi-physics simulation code and enable to track the gas-liquid surface. The simulation results are validated by the curve of flow regime for air-water under the adiabatic condition. The bubble and velocity of bubbles obtained by simulation results are analyzed.
4 bundle was implemented by using JUPITER in order to establish the evaluation method of the size and velocity of bubbles by the numerical simulation, which is the multi-physics simulation code and enable to track the gas-liquid surface. The simulation results are validated by the curve of flow regime for air-water under the adiabatic condition. The bubble and velocity of bubbles obtained by simulation results are analyzed.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2018-036, 216 Pages, 2019/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office, Fukushima Project Team and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Fukushima Technology Development and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each departments manage facilities and develop related technologies to achieve the "Middle-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2013 and 2014 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center and Quantum Beam Science Center, and activity of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Partitioning and Transmutation Technology Division, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center
JAEA-Technology 2017-033, 383 Pages, 2018/02
JAEA is pursuing research and development (R&D) on volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste. Construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is under planning as one of the second phase facilities in the Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC) program to promote R&D on the transmutation technology with using accelerator driven systems (ADS). The TEF consists of two facilities: ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) and Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). Development of spallation target technology and study on target materials are to be conducted in TEF-T with impinging a high intensity proton beam on a liquid lead-bismuth eutectic target. Whereas in TEF-P, by introducing a proton beam to minor actinide loaded cores, reactor physical properties of the cores are to be studied, and operation experiences of ADS are to be acquired. This report summarizes results of safety design for establishment permit of one of two TEF facilities, TEF-P.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro; Oi, Motoki; Harada, Masahide; Takada, Hiroshi; Kakishiro, Masanori*; Noguchi, Gaku*; Shimada, Tsubasa*; Seita, Kyoichi*; Murashima, Daisuke*; et al.
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 14, p.14 - 21, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)We developed an Au-In-Cd (AuIC) decoupler material to reduce induced radioactivity instead of Ag-In-Cd one, which has a cut off energy of 1eV. In order to implement it into an actual moderator-reflector assembly, a number of critical engineering issues need to be resolved with regard to large-sized bonding between AuIC and A5083 alloys by the hot isostatic pressing process. We investigated this process in terms of the surface conditions, sizes, and heat capacities of large AuIC alloys. We also show a successful implementation of an AuIC decoupler into a reflector assembly, resulting in a remarkable reduction of radioactivity by AuIC compared to AIC without sacrificing neutronic performance.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hutchinson, J.*; James, M.*; McKenzie, G.*; Sanchez, R.*; Oizumi, Akito; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 189, p.93 - 99, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:67.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worths was conducted in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb system and a low enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb system using the Comet Critical Assembly at NCERC. The critical experiments were designed to provide complementary data sets having different sensitivities to scattering cross sections of lead. The larger amount of the  U present in the LEU/Pb core increases the neutron importance above 1 MeV compared with the HEU/Pb core. Since removal of lead from the core shifts the neutron spectrum to the higher energy region, positive lead void reactivity worths were observed in the LEU/Pb core while negative values were observed in the HEU/Pb core. Experimental analyses for the lead void reactivity worths were performed with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP6.1 together with nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VII.1. The calculation values were found to overestimate the experimental ones for the HEU/Pb core while being consistent for the LEU/Pb core.
U present in the LEU/Pb core increases the neutron importance above 1 MeV compared with the HEU/Pb core. Since removal of lead from the core shifts the neutron spectrum to the higher energy region, positive lead void reactivity worths were observed in the LEU/Pb core while negative values were observed in the HEU/Pb core. Experimental analyses for the lead void reactivity worths were performed with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP6.1 together with nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VII.1. The calculation values were found to overestimate the experimental ones for the HEU/Pb core while being consistent for the LEU/Pb core.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kitamura, Seiji; Iwasaki, Akihisa*; Matsubara, Shinichiro*; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
To design fast reactor (FR) components, seismic response must be evaluated in order to ensure structural integrity. Therefore, a sophisticated analysis method has to be developed to study the seismic response of FR core. The fast reactors are made of several hundred core assemblies in hexagonal arrangement. When a big earthquake occurs, large horizontal displacement and impact force of each core assembly may cause a trouble for control rod insertability and core assembly intensity. Therefore, a seismic analysis method of fast reactor core considering horizontal nonlinear behavior, such as impact, fluid-structure interaction, etc. is needed. Validation of the core assembly vibration analysis code in three dimension (REVIAN-3D) was conducted by a full scale experiment. In this validation, the vertical behavior (raising displacement) and horizontal behavior (Impact force, horizontal response) of the analysis result agreed very well with the experiments.
Kikuchi, Norihiro; Imai, Yasutomo*; Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2017/07
In the design study of an advanced loop-type SFR in JAEA, a specific fuel assembly (FA) named FAIDUS (Fuel Assembly with Inner DUct Structure) has been adopted as one of the measures to enhance safety of the reactor. Thermal-hydraulics evaluations of FAIDUS under various operation conditions are required to confirm its design feasibility. In this study, after the applicability of ASFRE to FAs was confirmed through the numerical analysis using simulated FA tests, thermal-hydraulic analyses of a FA without an inner duct and a FAIDUS were conducted. Through the numerical analyses, it was indicated that asymmetric temperature distribution in a FAIDUS would not be occurred and characteristics of the temperature distribution was almost the same as that in a FA without an inner duct. Under the low flow rate condition, it was expected that the local flow acceleration caused by the buoyancy force in a FAIDUS could bring the flow redistribution and make the temperature distribution flat.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Yagi, Takahiro*; Pyeon, C.-H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(4), p.432 - 443, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:88.37(Nuclear Science & Technology)